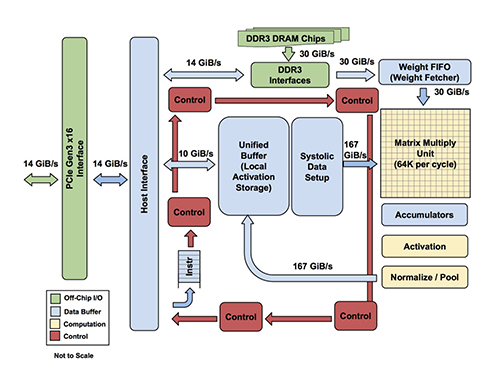
TPU (Tensor Processing Unit) from Google
A Tensor Processing Unit (TPU) is a specialized hardware processor developed by Google to accelerate machine learning. Unlike traditional CPUs or GPUs, TPUs are specifically designed to handle tensor operations, which account for most of the computations in deep learning models. This makes them incredibly efficient at those tasks and provides an enormous speedup compared to CPUs and GPUs. In this article, we’ll explore what a TPU is, how it works, and why they are so beneficial for machine learning applications.
1. What Are Tensor Processing Units (TPU)?
Tensor Processing Unit (TPU) is an application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) designed specifically for machine learning. In addition, TPUs offer improved energy efficiency, allowing businesses to reduce their electricity bills while still achieving the same results as processors with greater energy consumption. This makes them an attractive option for companies looking to use AI in their products or services. With the help of TPUs, businesses can develop and deploy faster, more efficient models that are better suited to their needs. TPUs offer a range of advantages over CPUs and GPUs. For instance, they provide up to 30x faster performsance than traditional processors and up to 15x better energy efficiency. This makes them ideal for companies looking to develop complex models in a fraction of the time. Finally, TPUs are more affordable than other specialized hardware solutions, making them an attractive option for businesses of all sizes.
Tensor Processing Units are Google’s ASIC for machine learning. TPUs are specifically used for deep learning to solve complex matrix and vector operations. TPUs are streamlined to solve matrix and vector operations at ultra-high speeds but must be paired with a CPU to give and execute instructions.
2. Is Google TPU faster than GPU?
GPUs have the ability to break complex problems into thousands or millions of separate tasks and work them out all at once, while TPUs were designed specifically for neural network loads and have the ability to work quicker than GPUs while also using fewer resources.
3. Key differences between TPU and GPU
-
Architecture: While GPUs use a flexible, general-purpose architecture, TPUs are purpose-built for machine learning tasks. GPUs consist of thousands of small cores designed to handle multiple tasks simultaneously, whereas TPUs have a more streamlined architecture focused on accelerating tensor operations.
-
Performance: When it comes to raw performance, TPUs have an edge over GPUs in certain scenarios. TPUs are designed to perform lower-precision calculations with higher throughput, which is often sufficient for training and inference tasks in neural networks. However, GPUs offer greater flexibility in terms of precision and can handle higher-precision computations when necessary.
-
Memory and Bandwidth: TPUs typically have a higher memory bandwidth than GPUs, which allows them to handle large tensor operations more efficiently. This results in faster training and inference times for neural networks. However, the amount of memory available on TPUs is generally lower than on GPUs, which can be a limiting factor for some applications.
4. Pros and Cons
GPU Pros |
Flexibility: GPUs can handle a wide range of tasks, including graphics rendering, simulations, and scientific computing, in addition to machine learning workloads. Maturity: GPUs have been widely adopted for deep learning, and there is a vast ecosystem of software and tools built around them, such as CUDA, cuDNN, and popular deep learning frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch. Precision: GPUs offer a range of precision options, from low-precision FP16 to high-precision FP64, making them suitable for various workloads with different accuracy requirements. |
GPU Cons |
Power Consumption: GPUs typically consume more power than TPUs, which can be a concern for large-scale deployments and energy efficiency. Cost: High-performance GPUs can be expensive, especially for small businesses or individual researchers. |
TPU Pros |
Performance: TPUs are designed specifically for tensor operations, resulting in faster training and inference times for neural networks compared to GPUs. Energy Efficiency: TPUs are more power-efficient than GPUs, making them a better choice for large-scale machine learning deployments. Ease of use: TPUs are integrated with popular machine learning frameworks like TensorFlow, making it easy for developers to leverage their capabilities. |
TPU Cons |
Limited Ecosystem: The TPU ecosystem is less mature than that of GPUs, with fewer software and tools available. Availability: TPUs are primarily available through Google Cloud Platform, which may not be suitable for all users and organizations. |
5. Is TPU faster than GPU for PyTorch?
TPUs typically have a higher memory bandwidth than GPUs, which allows them to handle large tensor operations more efficiently. This results in faster training and inference times for neural networks.
6. Applications for TPUs
Tensor Processing Units (TPUs) are specialized ASIC chips designed to accelerate the performance of machine learning algorithms. They can be used in a variety of applications, ranging from cloud computing and edge computing to machine learning or in various deep learning applications such as fraud detection, computer vision, natural language processing, self-driving cars, vocal AI, agriculture, virtual assistants, stock trading, e-commerce, and various social predictions By leveraging the power of TPUs, organizations can reduce costs and optimize their operations.
Cloud Computing: TPUs are used in cloud computing to provide better performance for workloads that require a lot of data processing. This allows businesses to process large amounts of data quickly and accurately at a lower cost than ever before. With the help of TPUs, businesses can make more informed decisions faster and improve their operational efficiency.
Edge Computing: TPUs are also used in edge computing applications, which involve processing data at or near the source. This helps to reduce latency and improve performance for tasks such as streaming audio or video, autonomous driving, robotic navigation, and predictive analytics. Edge computing also facilitates faster and more reliable communication between devices in an IoT network.
Machine Learning: TPUs are used to accelerate machine learning models and algorithms. They can be used to develop novel architectures that are optimized for tasks such as natural language processing, image recognition, and speech recognition. By leveraging the power of TPUs organizations can develop more complex models and algorithms faster. This will enable them to achieve better results with their machine-learning applications.
When to Use TPUs: Since TPUs are high specialized hardware for deep learning, it loses a lot of other functions you would typically expect from a general-purpose processor like a CPU. With this in mind, there are specific scenarios where using TPUs will yield the best result when training AI. The best time to use a TPU is for operations where models rely heavily on matrix computations, like recommendation systems for search engines. TPUs also yield great results for models where the AI analyzes massive amounts of data points that will take multiple weeks or months to complete. AI engineers use TPUs for instances without custom TensorFlow models and have to start from scratch.
When Not to Use TPUs: As stated earlier, the optimization of TPUs causes these types of processors to only work on specific workload operations. Therefore, there are instances where opting to use a traditional CPU and GPU will yield faster results. These instances include:
-
Rapid prototyping with maximum flexibility
-
Models limited by the available data points
-
Models that are simple and can be trained quickly
-
Models too onerous to change
-
Models reliant on custom TensorFlow operations written in C++
TPU Versions and Specifications |
|
TPUv1 |
The first publicly announced TPU. Designed as an 8-bit matrix multiplication engine and is limited to solving only integers. [.text-justify] |
TPUv2 |
Since engineers noted that TPUv1 was limited in bandwidth. This version now has double the memory bandwidth with 16GB of RAM. This version can now solve floating points making it useful for training and inferencing. [.text-justify] |
TPUv3 |
Released in 2018, TPUv3 has twice the processors and is deployed with four times as many chips as TPUv2. The upgrades allow this version to have eight times the performance over previous versions. [.text-justify] |
TPUv4 |
version of TPU produced on May 18, 2021. Google’s CEO announced that this version would have more than twice the performance of TPU v3. [.text-justify] |
TPUv5 |
This is the latest version of TPU on Dec 6, 2023. Compared to TPU v4, TPU v5p features more than 2X greater FLOPS and 3X more high-bandwidth memory (HBM),” Google said. The TPU v5p pods have 95GB of high-bandwidth memory, while the TPU v4 pods have 32GB of HBM. The HBM bandwidth of a TPU v5p pod is 2,765GBps, while the TPU v4 bandwidth was 1228GBps. |
Edge TPU |
This TPU version is meant for smaller operations optimized to use less power than other versions of TPU in overall operation. Although only using two watts of power, Edge TPU can solve up to four terra-operations per second. Edge TPU is only found on small handheld devices like Google’s Pixel 4 smartphone. |
| Benefits of the TPU Architecture | |
|---|---|
High Performance |
The TPU architecture is designed to maximize performance, ensuring that the processor can execute operations at extremely high speeds. |
Low Power Consumption |
Compared to CPUs and GPUs, the TPU architecture requires significantly less power consumption, making it ideal for applications in which energy efficiency is a priority. |
Cost Savings |
The TPU architecture is designed to be affordable, making it an attractive solution for businesses that are looking to reduce their hardware costs. |
Scalability |
The TPU architecture is highly scalable and can accommodate a wide range of workloads, from small applications to large-scale projects. |
Flexibility |
The TPU architecture is flexible and can be adapted to meet the needs of different applications, making it suitable for a range of use cases. |
Efficient Training |
The TPU architecture enables efficient training of deep learning models, allowing businesses to quickly iterate and improve their AI solutions. |
Security |
The TPU architecture is highly secure, making it an ideal solution for mission-critical applications that require high levels of security. |
Enhanced Reliability |
The TPU architecture has enhanced reliability, providing businesses with the assurance that their hardware will perform as expected in any environment. |
Easy to Deploy |
The TPU architecture is designed for easy deployment, allowing businesses to quickly set up and deploy their hardware solutions. |
Open Source Support |
The TPU architecture is backed by an open-source community that provides support and assistance when needed, making it easier for businesses to get the most out of their hardware investments. |
Improved Efficiency |
The TPU architecture is designed to optimize efficiency, allowing businesses to get the most out of their hardware resources and reducing the cost of running AI applications. |
End-to-End Solutions |
The TPU architecture provides a complete end-to-end solution for all types of AI projects, allowing businesses to focus on their development and operations instead of worrying about hardware compatibility. |
Cross-Platform Support |
The TPU architecture is designed to work across multiple platforms, making it easier for businesses to deploy their AI solutions in any environment. |
Future Ready |
The TPU architecture is designed with the future in mind, providing businesses with a solution that will remain up-to-date and ready to take on next-generation AI applications. |
Industry Standard |
The TPU architecture is becoming an industry standard for AI applications, giving businesses the confidence that their hardware investments are future-proofed. |
7. Google TPU v5e AI Chip
TPU v5e is also Google’s first AI chip integrated into a suite of software and tools for large-scale orchestration of AI workloads in virtual environments. The AI chip is now available in preview to Google Cloud customers.
The new AI chip succeeds the previous generation TPUv4, which was used to train the new large language models PaLM and PaLM 2 used in Google search, mapping and online productivity applications. The Cloud TPU v5e is also the first Google AI chip available outside the United States. TPUv4 was only available in North America. The TPU v5e computers will be installed in the Netherlands for EMEA markets and in Singapore for Asia-Pacific markets.
A researcher, Andrew B. Kahng of the University of California, San Diego, then reverse-engineered Google’s chip design techniques and found that human chip designers and automated tools were sometimes faster than the technique based solely on Google’s AI.
The performance numbers indicate that the TPU v5e is suited for inference rather than training. The chip delivers a peak performance of 393 teraflops of INT8 performance per chip, which is better than 275 petaflops on TPU v4.
The new Google TPU v5e is more efficient and more scalable than v4, according to Google. Multislice “enables users to easily scale AI models beyond the limits of physical TPU modules – up to tens of thousands of Cloud TPU v5e or TPU v4 chips,”. Google has also tweaked the virtual machines for TPU v5e so that the chips can process multiple virtual machines simultaneously. Google announced the availability of Kubernetes service for Cloud TPU v5e and v4, which will help orchestrate AI workloads on TPUs. Google said the largest configuration could deploy 64 virtual machines across 256 TPU v5e clusters. “This feature allows customers to choose the right configurations to serve a wide range of LLM and gen AI model sizes,” Google executives wrote.
 .pdf
.pdf