Mirrors
1. Overview
Mirrors are views that reference data in a possibly different memory space. They are used to access data in a different memory space without copying it.
Kokkos::View<double**, Space> view(...);
auto host_mirror = Kokkos::create_mirror_view(view);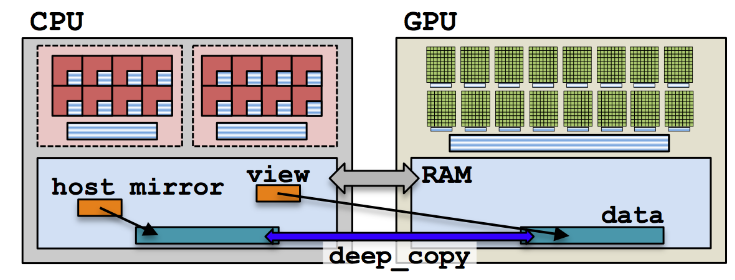
Two views are created: view in the memory space Space and host_mirror in the host memory space.
The data are copied back and forth between the two views using the Kokkos::deep_copy function.
2. Mirroring pattern
-
Create a
viewin a specific memory space.
Kokkos::View<double**, Space> view(...);-
Create a mirror view in the host memory space,
host_mirror.
auto host_mirror = Kokkos::create_mirror_view(view);-
Populate
host_mirrorwith data (from file, user input, etc.). -
Copy data from
host_mirrortoviewusingKokkos::deep_copy. -
Perform computations on
view:
Kokkos::parallel_for("Operation",
RangePolicy<Space>(0, view.extent(0)),
KOKKOS_LAMBDA(...) { /* use and change view */ }
);-
If nedded, copy data back to
host_mirrorusingKokkos::deep_copy.
Kokkos::deep_copy(host_mirror, view);
create_mirror_view allocates data only if the host process cannon access view 's data.
Otherwise, it returns a view that references the same data as view.
The command create_mirror makes always make data allocation.
|
3. Example
We present the example 04 from the tutorial of Kokkos.
typedef Kokkos::View<double*, Kokkos::LayoutLeft, MemSpace> ViewVectorType;
typedef Kokkos::View<double**, Kokkos::LayoutLeft, MemSpace> ViewMatrixType;
ViewVectorType y( "y", N );
ViewVectorType x( "x", M );
ViewMatrixType A( "A", N, M );
// Create host mirrors of device views.
ViewVectorType::HostMirror h_y = Kokkos::create_mirror_view( y );
ViewVectorType::HostMirror h_x = Kokkos::create_mirror_view( x );
ViewMatrixType::HostMirror h_A = Kokkos::create_mirror_view( A );Kokkos::deep_copy( y, h_y );
Kokkos::deep_copy( x, h_x );
Kokkos::deep_copy( A, h_A );Then the code computes the quantity \(\left<y, Ax\right>\).
The full code is present in the file 05_kokkos_mirrors.cpp.
3.1. Performance comparisons
On gaya:
./kokkos_mirros -nrepeat 1000
Total size S = 4194304 N = 4096 M = 1024
Kokkos::HostSpace
Computed result for 4096 x 1024 is 4194304.000000
N( 4096 ) M( 1024 ) nrepeat ( 1000 ) problem( 33.5954 MB ) time( 0.323193 s ) bandwidth( 103.949 GB/s )On gaya-gpu:
./kokkos_mirros -nrepeat 1000
Total size S = 4194304 N = 4096 M = 1024
Kokkos::HIPSpace
Computed result for 4096 x 1024 is 4194304.000000
N( 4096 ) M( 1024 ) nrepeat ( 1000 ) problem( 33.5954 MB ) time( 0.485132 s ) bandwidth( 69.25 GB/s ) .pdf
.pdf