Introduction
Managing a building’s thermal performance is important for sustainable design and energy efficiency. It plays a significant role in ensuring the comfort and health of occupants while also influencing operational costs and the ecological footprint of the building. As green building becomes more popular and energy prices go up, improving how a building handles heat is becoming more necessary.
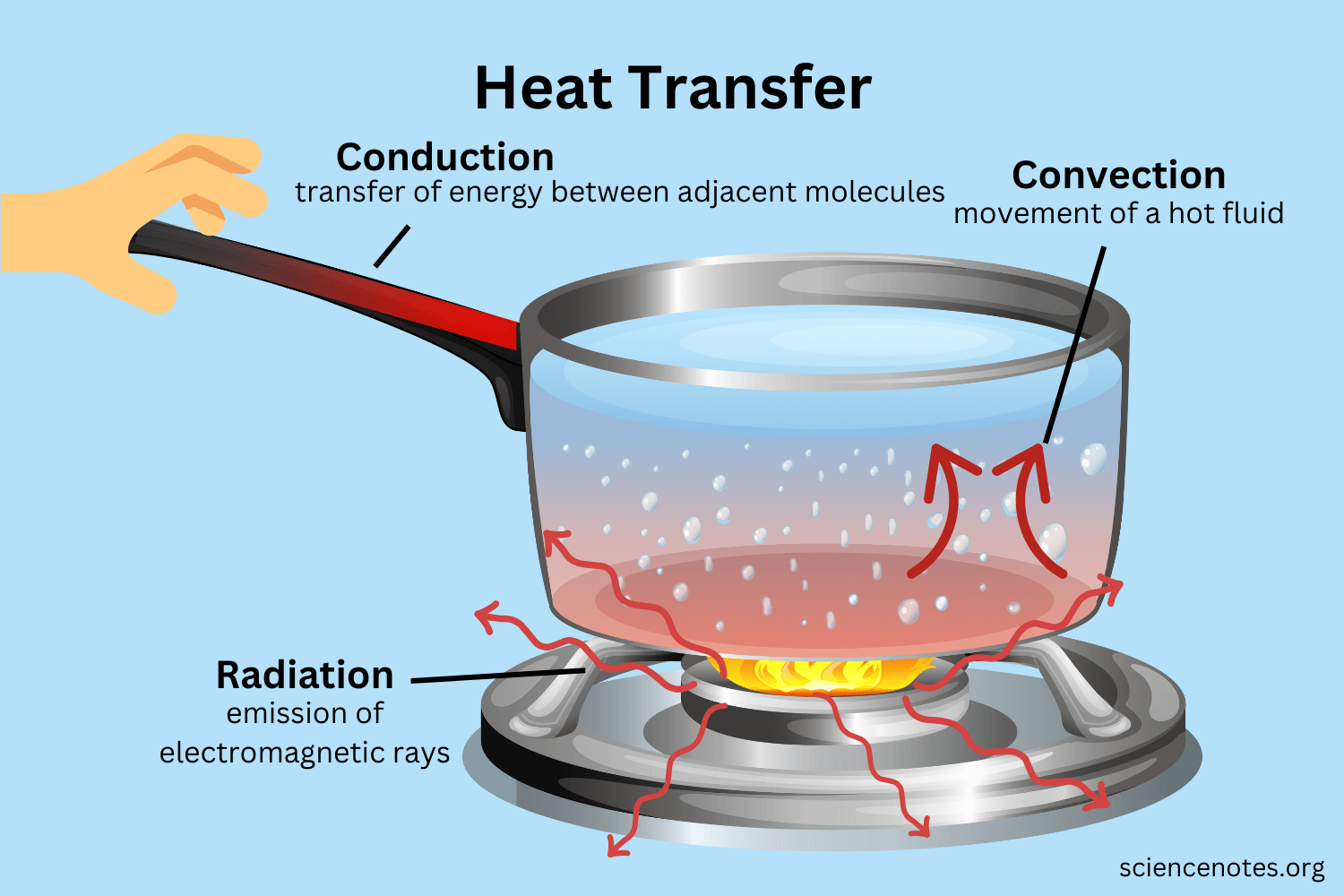
Heat equations are key to dealing with the challenges of managing heat. They help explain how heat moves and spreads in a material or space. Thermal analysis is done to predict temperatures and heat transfer in and around objects. This helps in understanding things like stresses caused by heat or how heat affects fluid flow in solidifying metal. Heat flow has been categorised into three different modes.
-
Conduction : is heat transfer directly between neighboring atoms or molecules. Usually, it is heat transfer through a solid. For example, the metal handle of a pan on a stove becomes hot due to convection. Touching the hot pan conducts heat to your hand
-
Convection : is heat transfer via the movement of a fluid, such as air or water. Heating water on a stove is a good example. The water at the top of the pot becomes hot because water near the heat source rises. Another example is the movement of air around a campfire. Hot air rises, transferring heat upward. Meanwhile, the partial vacuum left by this movement draws in cool outside air that feeds the fire with fresh oxygen.
-
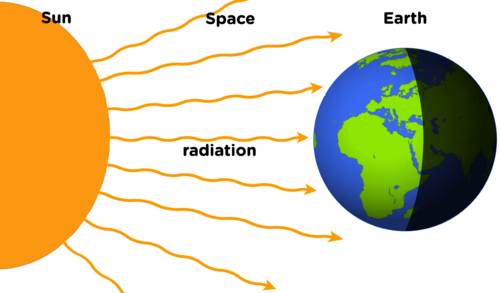
Radiation : is the emission of electromagnetic radiation. While it occurs through a medium, it does not require one. For example, it’s warm outside on a sunny day because solar radiation crosses space and heats the atmosphere. The burner element of a stove also emits radiation. However, some heat from a burner comes from conduction between the hot element and a metal pan. Most real-life processes involve multiple forms of heat transfer.
 .pdf
.pdf