Application
1. Triangular cavity
The dimensions of this geometry and explanation are provided in the following section: Case : Triangular Cavity:
The required temperatures (fluxes) are imposed as Dirichlet (Neumann) boundary conditions on the external surfaces of the rectangles which are parallel to the cavity boundaries. Homogeneous Neumann conditions are imposed on the remaining surfaces of the rectangles(you can see all the parameters here).
After execution, to view a table of different results, open the file located at
/feelppdb/triangular_cavity_insulation/np_1.
You can visualize the results in ParaView
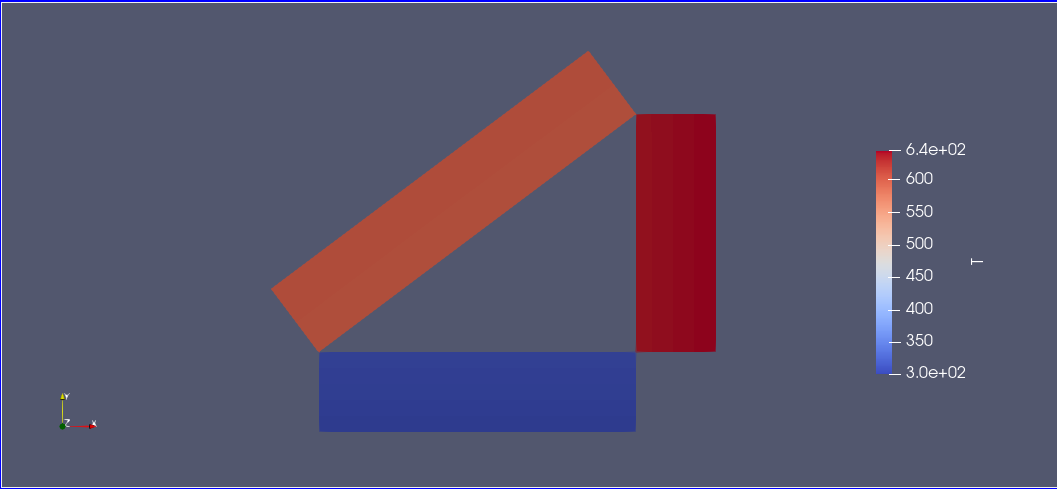
2. Rectangular cavity
The dimensions of this geometry and explanation are provided in the following section: Case : Rectangular Cavity:
The required temperatures (fluxes) are imposed as Dirichlet (Neumann) boundary conditions on the external surfaces of the rectangles which are parallel to the cavity boundaries. Homogeneous Neumann conditions are imposed on the remaining surfaces of the rectangles(you can see all the parameters here).
After execution, to view a table of different results, open the file located at
/feelppdb/rectangular_cavity_insulation/np_1.
You can visualize the results in ParaView
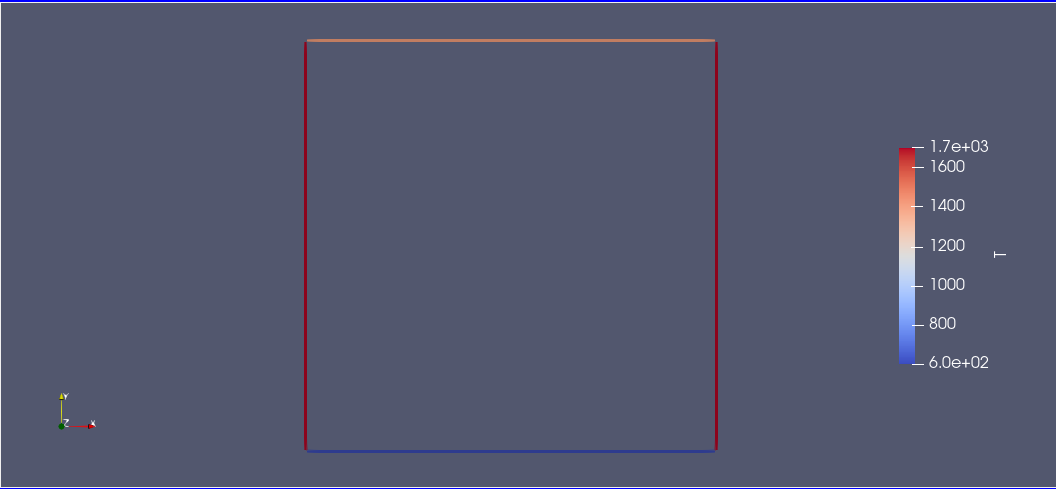
3. Cylindrical cavity
The dimensions of this geometry and explanation are provided in the following section: Case : Cylindrical Cavity:
The required temperatures are imposed as Dirichlet boundary conditions on the external surfaces which are parallel to the cavity boundaries. Homogeneous Neumann conditions are imposed on the remaining surfaces(you can see all the parameters here).
After execution, to view a table of different results, open the file located at
/feelppdb/rectangular_cavity_insulation/np_1.
You can visualize the results in ParaView
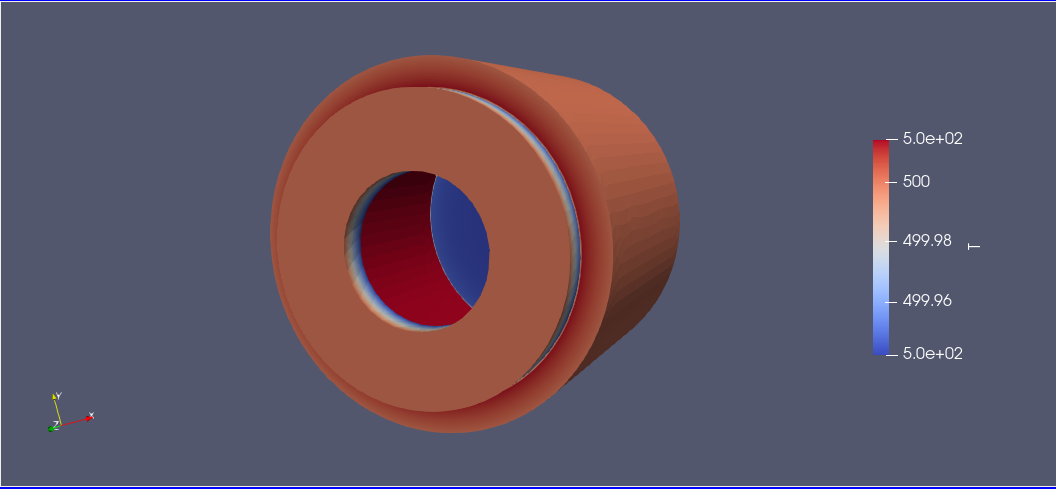
 .pdf
.pdf