Ray Tracing
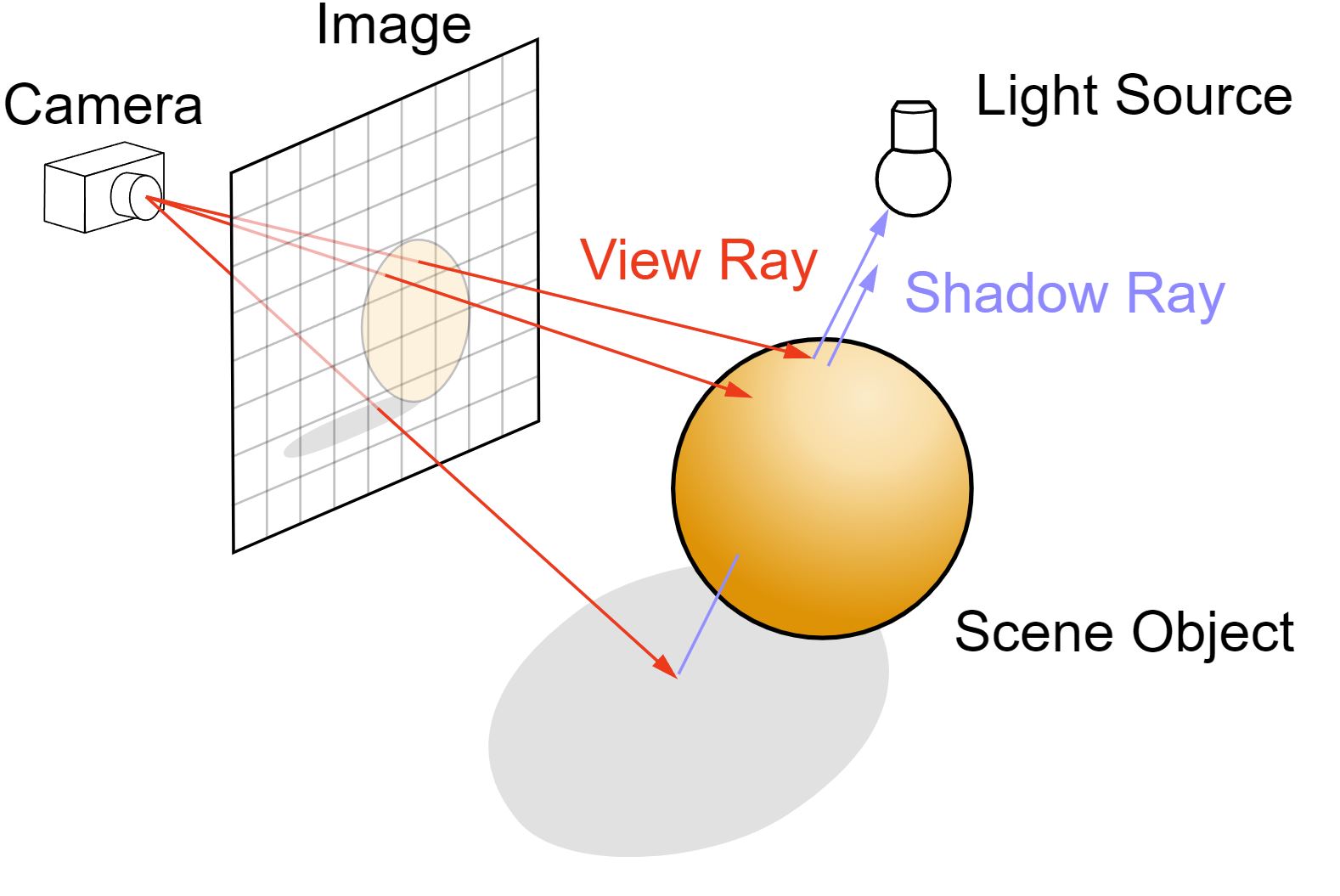
A ray tracer is software that allows the visualization of a 3D modeled scene based on the theory of inverse geometric optics. The objective is to launch rays from a point of observation (a camera) and follow the inverse optical path of this ray. When there is an intersection between the ray and an object in the environment, a shading calculation determines if the intersected object is illuminated by a light source and evaluates the color that it will reflect and transmit towards the point of observation.
1. The Equation of a Ray
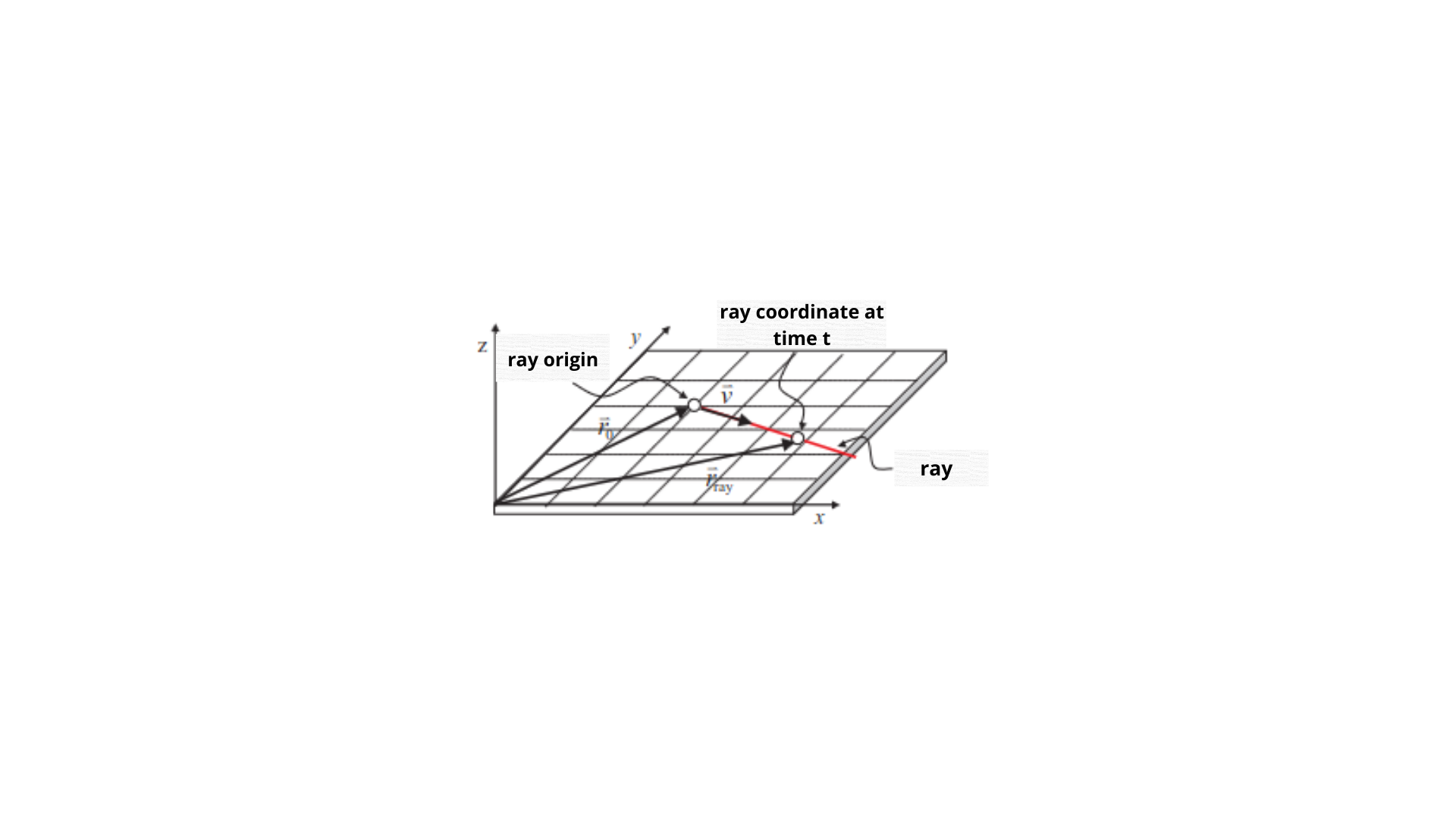
A ray $\vec{r}_{\text {my }}$ is a structure with an origin $\vec{r}_0$ and a direction $\vec{v}$. It allows for the calculation of intersections with geometric shapes in a scene. A time parameter $t$ is used to chronologically order the ray’s intersections with objects in the scene.
A ray parameterized over time has the following form:
where
$ \vec{r}_{\text {ray }}$ : Coordinate hit by the ray after a time $t$.
$\vec{r}_0:$ Origin of the ray.
$\bar{v}$ : Direction of the ray $(\|\bar{v}\|=1$, unit vector $)$.
$t$ : Time elapsed in the ray’s movement.
In computing, the definition of a ray will need the following variables:
| Ray Geometry | Information on the intersected geometry |
|---|---|
Origin position of the ray (\(\bar{r}_0\)) Direction of the ray (\(\bar{v}\)) |
The time \(t\) to intercept the geometry. The normal to the surface \(\bar{n}\) at the interception site. A texture coordinate \(uv\) (if any). Reference to the material applied on the geometry (e.g., to obtain the color of the geometry). |
In this part of the code, we define the components of a ray
template <int RealDim>
class BVHRay
{
public:
using vec_t = eigen_vector_type<RealDim>;
BVHRay(vec_t const& orig, vec_t const& dir,
double dmin = 0, double dmax = std::numeric_limits<double>::max() )
:
M_origin( orig ),
M_dir( dir ),
M_distanceMin( dmin ),
M_distanceMax( dmax )
{}
BVHRay() : BVHRay(vec_t::Zero(),vec_t::Zero()) {}
BVHRay( BVHRay const& ) = default;
BVHRay( BVHRay &&) = default;
BVHRay& operator=( BVHRay && ) = default;
BVHRay& operator=( BVHRay const& ) = default;
vec_t const& origin() const noexcept { return M_origin; }
vec_t const& dir() const noexcept { return M_dir; }
double distanceMin() const { return M_distanceMin; }
double distanceMax() const { return M_distanceMax; }
private:
friend class boost::serialization::access;
template <class Archive>
void serialize( Archive& ar, const unsigned int version )
{
ar & M_origin;
ar & M_dir;
ar & M_distanceMin;
ar & M_distanceMax;
}
private:
vec_t M_origin, M_dir; // ray origin and dir
double M_distanceMin, M_distanceMax;
};
2. Ray-sphere intersection
-
Condition I:point is on ray
-
Condition 2: point is on sphere
-
Let be a sphere of radius r, the ray intersects the sphere so
-
Substitute:
-
this is a quadratic equation in $t$
-
Solution for $t$ by quadratic formula:
-
simpler form holds when $\mathbf{d}$ is a unit vector.
For more explanation, see here.
In this method of template intersect we compute intersection with a ray from the BVH built and return a vector of intersection result
template<typename... Ts>
auto intersect( Ts && ... v )
{
auto args = NA::make_arguments( std::forward<Ts>(v)... );
auto && ray = args.get(_ray);
bool useRobustTraversal = args.get_else(_robust,true);
IntersectContext ctx = args.get_else(_context,IntersectContext::closest);
bool parallel = args.get_else(_parallel,this->worldComm().size() > 1);
bool closestOnly = ctx == IntersectContext::closest;
using napp_ray_type = std::decay_t<decltype(ray)>;
if constexpr( std::is_same_v<BVHRaysDistributed<nRealDim>,napp_ray_type> ) // case rays distributed on process
{
// WARNING: this algo is not good (all_gather of rays then all run bvh), just a quick version for test
auto const& localRays = ray.rays();
std::vector<int> resLocalSize( this->worldComm().size() );
mpi::all_gather( this->worldComm(), (int)localRays.size(), resLocalSize );
std::vector<ray_type> raysGathered;
if ( this->worldComm().isMasterRank() )
{
int gatherRaySize = std::accumulate( resLocalSize.begin(), resLocalSize.end(), 0 );
raysGathered.resize( gatherRaySize );
}
mpi::gatherv( this->worldComm(), localRays, raysGathered.data(), resLocalSize, this->worldComm().masterRank() );
mpi::broadcast( this->worldComm(), raysGathered, this->worldComm().masterRank() );
auto intersectGlobal = this->intersect(_ray=raysGathered,_robust=useRobustTraversal,_context=ctx,_parallel=true);
std::vector<std::vector<rayintersection_result_type>> res;
res.resize( ray.numberOfLocalRay() );
std::size_t startRayIndexInThisProcess = 0;
for ( int p=0;p<this->worldComm().rank();++p )
startRayIndexInThisProcess += resLocalSize[p];
std::copy_n(intersectGlobal.cbegin()+startRayIndexInThisProcess, localRays.size(), res.begin());
return res;
}
else if constexpr ( is_iterable_v<std::decay_t<decltype(ray)>> ) // case rays container are identical all on process (TODO: internal case)
{
std::vector<std::vector<rayintersection_result_type>> resSeq;
resSeq.reserve( ray.size() );
for ( auto const& currentRay : ray )
{
auto currentResSeq = this->intersectSequential( currentRay,useRobustTraversal );
if ( closestOnly && currentResSeq.size() > 1 )
currentResSeq.resize(1);
resSeq.push_back( std::move( currentResSeq ) );
}
if ( !parallel )
return resSeq;
mpi::all_reduce( this->worldComm(), mpi::inplace( resSeq ), [](auto const& x, auto const& y) -> std::vector<std::vector<rayintersection_result_type>> {
std::size_t retSize = x.size();
std::vector<std::vector<rayintersection_result_type>> ret;
DCHECK( x.size() == y.size() ) << "not same size x:" << x.size() << " y:" << y.size();
ret.reserve( retSize );
for ( int k = 0; k < retSize ; ++k )
{
auto const& a = x[k];
auto const& b = y[k];
if ( a.empty() )
ret.push_back( b );
else if ( b.empty() )
ret.push_back( a );
else
{
// WARNING only return one intersection (closest or anyhint)
if ( a.front().distance() < b.front().distance() )
ret.push_back( a );
else
ret.push_back( b );
}
}
return ret;
} );
return resSeq;
}
else // only one ray (all process should have the same ray if parallel=true)
{
auto resSeq = this->intersectSequential( ray,useRobustTraversal );
if ( closestOnly && resSeq.size() > 1 )
resSeq.resize(1);
if ( !parallel )
return resSeq;
}
}
 .pdf
.pdf